Bitcoin transaction fees have gotten ridiculously high but luckily a better solution is on its way. The Lightning Network is a system that would be built on top of the existing Bitcoin network and allow people to perform transactions instantly and at much lower fees, freeing up the main network in the process.
How the Lightning Network works
We talked about smart contracts in our Ethereum guide, so we recommend you go ahead and read it to get a general idea on how they work. The Lightning Network is also based on smart contracts and built on top of the existing Bitcoin blockchain to allow for speedy payments with low transaction fees between any two parties. For such a transaction to take place, there are a few steps that need to be taken.
Firstly, there must be a multi-signature wallet set up holding some bitcoin – at least the sender or recipient should have one. That wallet’s address will be saved to the Bitcoin blockchain, including a smart contract showing exactly who owns how much of the bitcoin deposited in this wallet.
After the payment channel is configured, the two parties will be able to perform as many transactions as they want (between each other) with no need to access the blockchain stored data anymore. After each transaction, the balance sheet will be updated although it won’t be uploaded to the blockchain. Instead, both parties will keep a copy of it. Should the payment channel get closed or a dispute occurs, the two parties can use the latest mutually signed balance sheet to pay from their multi-signature wallet.
This might seem very complicated, but certainly not to the end-user as the entire process takes place automatically in the background. Even though you may not understand all the intricacies of performing transactions via the Lightning Network, it’s easy to see the public blockchain is hardly used and the two parties will track the payments themselves. In return, the transactions will be much faster, and the fees lower.
Source: emchat.net
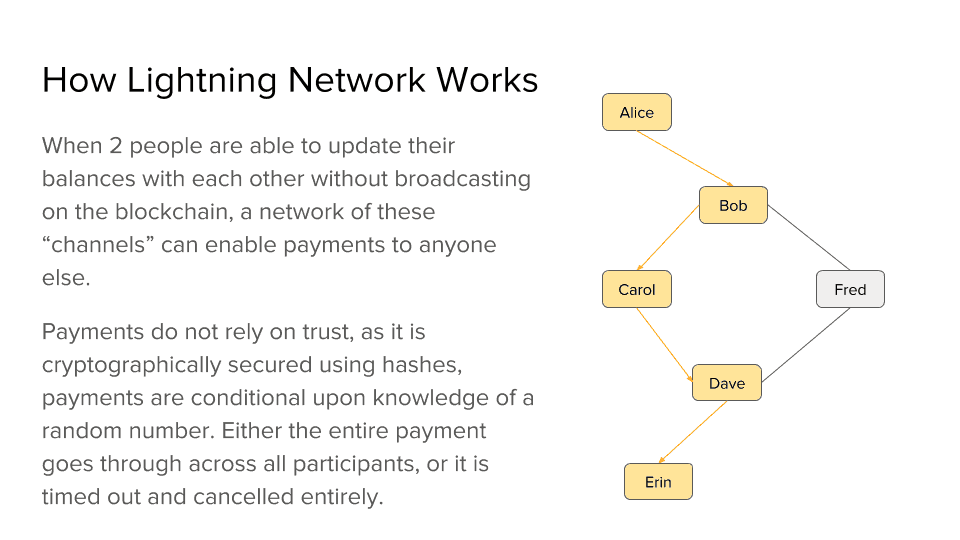
Keep in mind this is a network so it works just as it should. This means you won’t need to open a payment channel for each new party you want to transact with. If Alice needs to send some bitcoins to Erin, but she only has a payment channel with Bob, she can transfer the funds using one or more people’s existing channels through multiple hops.
Basically, the network needs just a few nodes to connect everyone. Even more, there are incentives for running connecting nodes as those who do it would be rewarded with small fees when transactions use one of their connections.
Because it is based on smart contracts, the Lightning Network will always ensure the funds reach their destination, and if there is no indirect path that can be taken, a refund will be issued. It’s also work mentioning the “nodes” only process the transactions and cannot control the funds they help transfer.
The Lightning Network pros and cons
As with any new system, there are some benefits, as well as shortcomings so let’s see what both are.
Pros
- Fractional payments: With the Lightning Network, the fees are proportional to the transferred amount so it allows tiny payments to the fraction of a cent.
- Instant payments: The funds are transferred in less than a second, the time needed to cross the network to your destination and back.
- Enhanced privacy: Data is stored on the blockchain only when the payment channel is opened and eventually closed. The rest of the transactions are stored by the two parties.
Cons
- Only online: You can’t transact with someone who is offline
- Centralization: Payment hubs might be encouraged (similar to mining pools).
- Peer failures: Should a peer be unresponsive it could take a long time (as much as hours) to close the payment channel and resend the funds through a new, valid route.
- Not optimized for large payments: Despite a valid route being available between multiple payment channels, the funds available in the peers multi-signature wallets might not be enough to transfer large funds.
Bitcoin Lightning Network release date
Right now, the Lightning Network is still being tested. On March 16th, Lightning Labs announced a new mainnet release of their Lightning Network implementation. Furthermore, ACINQ, a Bitcoin technology company, has announced the first version of eclair for mainnet (their own Lightning network implementation) less than a week ago.
For now, we don’t have an official date when the Lightning Network will be launched on the Bitcoin Mainnet and integrated into major wallets but there’s a good chance it will happen this year.